Asynchronous programming is essential when working with APIs that require network requests, as it prevents blocking your application while waiting for responses. The OpenAI Chat Completion API is widely used for chatbot applications, AI-powered assistants, and content generation. In this article, we will explore how to efficiently make async API calls to OpenAI's Chat Completion API using Python's asyncio and the official openai package.
Why Use Async for API Calls?
When making API calls, especially to services like OpenAI that may take a few seconds to respond, synchronous requests can significantly slow down applications, particularly when handling multiple requests. Using async and await, we can:
- Improve performance by making concurrent requests.
- Avoid blocking execution while waiting for responses.
- Enhance scalability for applications that need to handle multiple API requests simultaneously.
The openai Python package has supported asynchronous programming with async/await for a long time, making it efficient and straightforward to use.
Let's start with a basic example and then move on to a more advanced implementation.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the code, ensure you have the following installed:
pip install --upgrade openaiYou'll also need an OpenAI API key. If you don't know how to obtain one, see this article: How to create a new OpenAI API key
Basic Example: Single Async Request
In this example, we'll make a single async request to the OpenAI Chat Completion API using the openai package.
import asyncio
import openai
import os
# Use your actual OpenAI API key here
# You can directly set it like this: OPENAI_API_KEY = "your key here"
# Or you can use an environment variable like this: OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
from config import OPENAI_API_KEY
async def get_chat_response(prompt):
client = openai.AsyncOpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
async def main():
prompt = "What is the capital of Vietnam?"
result = await get_chat_response(prompt)
print(result)
# Execute the main function
asyncio.run(main())You'll get an output like this:
The capital of Vietnam is Hanoi.Explanation:
- The
get_chat_responsefunction initializes theAsyncOpenAIclient and sends an async request to OpenAI. - The API response is returned as a JSON object.
- The
mainfunction callsget_chat_responseand prints the response. - The script is executed using
asyncio.run().
Advanced Example: Handling Multiple Requests Concurrently
For applications requiring multiple OpenAI requests (e.g., batch processing, chatbot conversations), handling them concurrently is crucial. Here’s how we can do that using asyncio.gather.
import asyncio
import openai
import os
# Use your actual OpenAI API key here
# You can directly set it like this: OPENAI_API_KEY = "your key here"
# Or you can use an environment variable like this: OPENAI_API_KEY = os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY")
from config import OPENAI_API_KEY
async def get_chat_response(client, prompt):
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
async def process_multiple_requests(prompts):
client = openai.AsyncOpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
tasks = [get_chat_response(client, prompt) for prompt in prompts]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
return results
async def main():
prompts = [
"Tell me a joke about AI.",
"Explain the theory of relativity in simple terms.",
"How do you make an HTTP request in Python?"
]
responses = await process_multiple_requests(prompts)
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"Response {i+1}: {response}")
# Execute the main function
asyncio.run(main())The output is pretty long so I didn't fully place it here. You can see the results on your own.
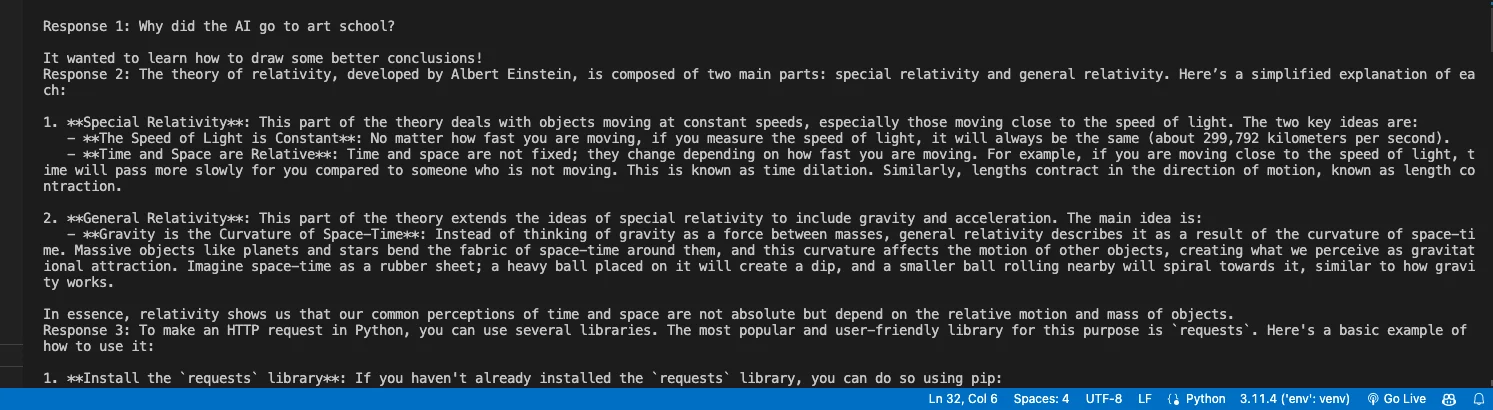
Explanation:
- We define
process_multiple_requeststo take a list of prompts and create async tasks for each request. - Using
asyncio.gather, we run all tasks concurrently, improving efficiency. - Each response is printed with its corresponding prompt.
Optimizing Performance
When dealing with multiple requests, consider:
- Rate Limiting: OpenAI enforces rate limits, so you may need to introduce delays (
asyncio.sleep()) or handle retries. - Error Handling: Implement error handling to catch network failures or API errors.
- Streaming Responses: OpenAI supports response streaming, reducing latency.
Handling Rate Limits
If you exceed OpenAI's rate limits, you can introduce a semaphore to limit the number of concurrent requests:
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(5) # Limit to 5 concurrent requests
async def get_chat_response(client, prompt):
async with semaphore:
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
temperature=0.7
)
return response.choices[0].message.contentConclusion
Using async API calls with OpenAI’s Chat Completion API significantly enhances performance and scalability. The openai package has supported async/await for a long time, making it a robust choice for building efficient AI applications. The basic example helps understand the foundation, while the advanced example demonstrates concurrent requests efficiently. Implementing these techniques ensures smooth interactions with OpenAI’s API, making applications more responsive and efficient.